What is EMI?
An Equated Monthly Installment is a fixed monthly amount paid by a borrower to the lender over a specific loan tenure. EMI covers the payment of both the principal and interest. It ensures that the loan amount is fully paid off.
It is prudent to consider all repayment aspects before applying for a home loan. This means factoring in how much you can shell out for an Equated Monthly Installment and, most importantly, how long you can go on repaying it to complete the full repayment of the borrowed amount.
All banks and Home Finance Companies have their individual schemes to disburse home loans and offer convenient repayment packages and tenure. It depends on you (the borrower) to choose the one that suits your repayment capacity without weighing you down.
SHORTER TENURE, FASTER PRINCIPAL REPAYMENT: When you choose a shorter home loan repayment tenure, it also means you have the scope to repay your principal amount much faster. This is because your EMI amount is higher. Since the interest is calculated on the outstanding principal amount, a faster principal repayment leads to lower absolute interest payout.
LONGER TENURE, LESSER EMI AMOUNT: A few years ago, there were a few banks and HFCs that offered a long home loan repayment tenure. Today, with a surfeit of financial establishments, both public sector enterprises and private entities, in the country, borrowers have a wide choice to pick from. With competitive interest rates offered on a platter, borrowers can opt for long home loan repayment tenure (as long as 30 years). A longer tenure gives you the opportunity to pay lesser EMI amounts that make it easier on your pocket, thus giving you more scope to plan your investments and other loans.
INCREASE YOUR EMI AMOUNT: You have probably been paying your EMIs based on how much you can spare from your earnings. To bring down your principal amount, you can also opt to increase your EMI amount every year. This option depends on whether you expect your earnings to increase each year. If you are a salaried person and expect a raise in your annual income every year, you have the liberty to scale up your EMI amount. For example, if you expect a five or 10 per cent increase in your salary, you can increase your EMI amount by five or 10 per cent. This will not only lower your repayment time, but also bring down your total interest cost.
PREPAYMENT: Home loan prepayment is an excellent way to bring down your outstanding loan amount and save on your net interest. But you need to work practically and sensibly to continue making your payments with discipline, and in a way that does not pose as a burden on your finances. If you are a salaried person expecting a consolidated and confirmed increment amount from your company, such as an annual bonus, target variable pay, leave travel allowance, etc, it makes sense to stick to a systematic prepayment plan for a quarterly or half yearly slab.
First, check with your bank about a prepayment penalty or charges. Many banks levy a prepayment fee, which could topple your planning cart. So, try and weigh the options before taking the prepayment plunge.
The perks of loan prepayment give you a dual benefit of tax savings and savings on net interest paid.
Many people opt for a longer loan tenure for the sake of lower EMIs. However, a longer tenure comes with a pitfall of massive interest repayment that will go through the EMIs. Let’s assume you earn Rs.60,000 net per month and are seeking a 25-year home loan of Rs.35 lakh at an interest rate of 8.60 per cent per annum. However, if you choose a 20-year loan, what will the status be then?
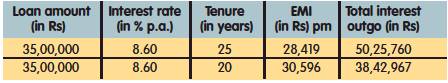
So, you can save around Rs.11, 82,793 of interest by choosing a shorter tenure of 20 years at an expense of a slightly higher EMI of Rs.2,177.
THE LOAN: INCOME RATIO There should be a good balance between debt and income. The proposed EMI must ideally not exceed 30-40 per cent of your net monthly income, especially if you have only one dedicated source of income. And if you have varied sources of income, your EMI must not exceed 50-60 per cent of your net monthly income.




